Activities / Results
2017/12/13
Interactive Reinforcement Learning based Assistive Robot
As robots enter people's daily lives, the tasks assigned by robots are complicated and various, and the needs of people interacting with robots are also diverse. Besides, this study proposes a learning strategy for service delivery models. Through the human feedback, this strategy enables robots to understand users’ needs and preferences in order to adjust their behavior. Hence, we assume that user needs and preferences may change over time. To sum it up, the purpose of this article is to adapt the behavior of the robot to these changes. That is to say, the robot's service delivery model can also be adjusted online. In addition, it can choose a new action from those favorable actions that were chosen long time ago, or it can choose an act that has not recently made people's feeling uncomfortable. In order to make our system into practice, the service robot in question is applied to the social environment.
The purpose of robot-assisted human robot interaction (HRI) is usually to understand the user's needs and intentions. In this research, we ‘ll apply the ability of the machine learning technique within the service tasks. In addition, the goal of the robot is to provide personalized services for individual user. As shown in Figure 1, we build a task model so that the robot can understand the needs and preferences of users in the process of interacting with people.
The goal of the robot is to provide the service that the user expects at the right time and in the right situation. We have designed several types of services, each type can deliver with a different user preferences . For example, our robots can not only provide tea service, but also they can know the type of tea that users would like by themselves. By interacting with users and observing feedback, the robot should learn how to adapt to the user’s preference in order to deliver the appropriate actions. In the end, the robot will know to indicate which service the user would like. As shown in Figure 2, different users have their own needs and preferences. Additionally, user needs and preferences may change over time. Most importantly, the user does not directly tell the robot their preferences, or when to do the actions, the robot should learn itself by interacting with the user and adjust its behavior to suit different users. In the beginning, the robot knew nothing about the user's needs and preferences. Based on the collected interactive experience, the robot gradually understands the user, adjusts its behavior, and makes the interaction and service more efficient.
The purpose of robot-assisted human robot interaction (HRI) is usually to understand the user's needs and intentions. In this research, we ‘ll apply the ability of the machine learning technique within the service tasks. In addition, the goal of the robot is to provide personalized services for individual user. As shown in Figure 1, we build a task model so that the robot can understand the needs and preferences of users in the process of interacting with people.
The goal of the robot is to provide the service that the user expects at the right time and in the right situation. We have designed several types of services, each type can deliver with a different user preferences . For example, our robots can not only provide tea service, but also they can know the type of tea that users would like by themselves. By interacting with users and observing feedback, the robot should learn how to adapt to the user’s preference in order to deliver the appropriate actions. In the end, the robot will know to indicate which service the user would like. As shown in Figure 2, different users have their own needs and preferences. Additionally, user needs and preferences may change over time. Most importantly, the user does not directly tell the robot their preferences, or when to do the actions, the robot should learn itself by interacting with the user and adjust its behavior to suit different users. In the beginning, the robot knew nothing about the user's needs and preferences. Based on the collected interactive experience, the robot gradually understands the user, adjusts its behavior, and makes the interaction and service more efficient.
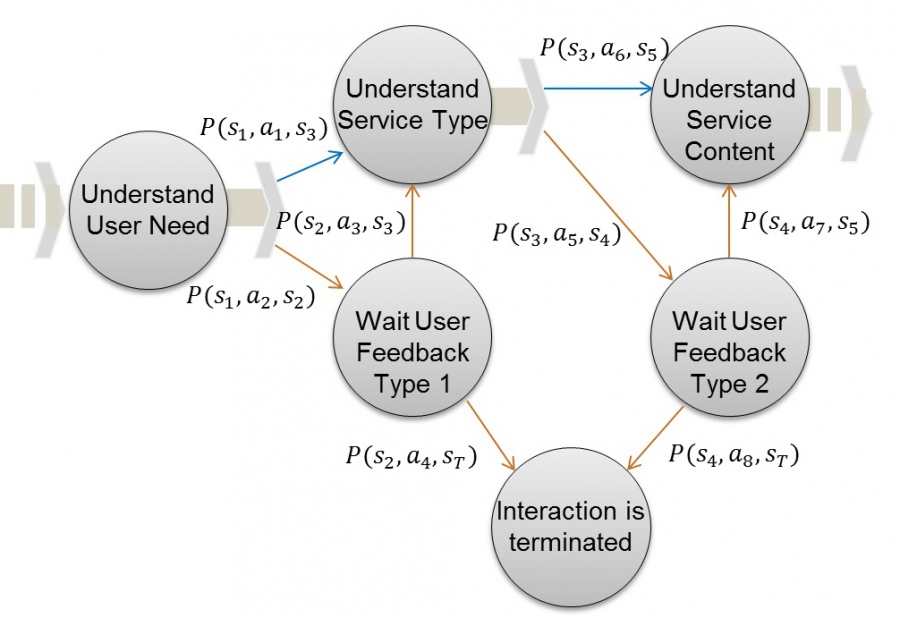
Fig. 1 Markov Decision Processes

Fig. 2 Human Robot Interaction Learning Processes